1. dec. 2024
Cryptography is a way of securing confidential or private information and making them inaccessible to unwanted individuals. It combines mathematical algorithms and hashing functions to ensure maximum security. The security standards are quickly changing with the rapid developments in technology.
The word cryptography may sound mysterious at first, but when you understand that it’s nothing more than a collection of algorithms, which makes the blockchain technology secure, it becomes much clearer. This blog post aims to serve as an introduction to this topic to let you understand the new terms and the inner workings of cryptography.
The evolution of cryptography
Cryptography isn’t anything new, as it has existed for centuries. It has adapted and transformed from simple secret codes to complex algorithms, which only advanced computers with enormous resources can even attempt to break. In ancient times, cryptography was as simple as shifting letters in the alphabet—yes, the Caesar Cipher. Simple, but effective for those times. Afterwards, World War II saw the creation and use of machines such as Enigma. Today, cryptography has evolved into advanced algorithms, which make it possible for a secure exchange of information without exposing the details to unwanted parties. Cryptography is used everywhere. Although it may not be immediately apparent to you as a user, cryptography plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety of your data and funds.
Why we trust the digital world
Every time you make a payment or send a message, encryption algorithms are behind the scenes. What they do is encrypt your data, making it impossible for bad actors to read or understand. To access and unlock the meaning, you need a key. It functions similarly to a letter left in a mailbox. Don’t have the key? Can’t read the letter.
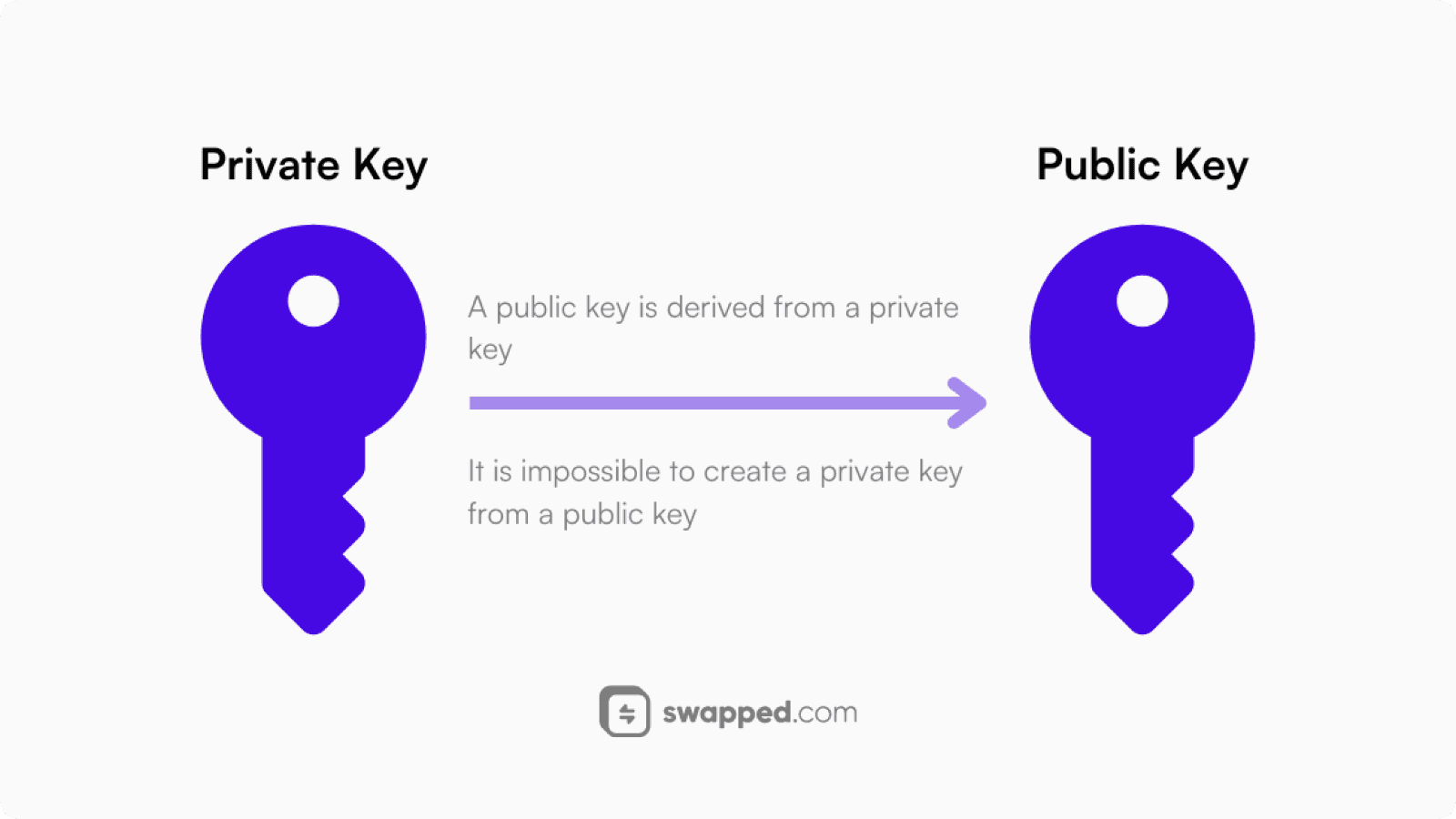
Public and private keys
Let’s imagine a scenario where you send a message to a friend. In order for it to be properly encrypted and arrive safely, you need two kinds of keys: a public key and a private one. These keys aren’t physical; they’re digital and consist of long strings of random numbers and letters.
Think of your public key as a mailbox on the street. Anyone can drop a letter in your mailbox, but only you can take it out and read it. You share the public key with anyone, so they can send you a secure and encrypted message.
The private key should be your best-kept secret, because this is what opens your mailbox. If you lose it by accident or someone steals it, everything you value is unlocked, ready to be taken away.
A private key controls all your assets. Make sure to keep it safe!
How hashing works
Hashing is another form of cryptography, which takes the input and converts it into a fixed-length string of characters. There’s a caveat to it, however, as the whole process is irreversible. The only way to see if your input and hash are corresponding is to compare two hashes side by side.
Example of hashing
Consider the sentence, "Cryptography is powerful". Using a simple hashing algorithm, this sentence might translate to:
c5b6f3f52a1be430f50e4b72c98d7cf2e4d1d01e5a8398b00b3d941f46e3035e
If you change even a small part of the sentence, like "Cryptography is fun", the hash would look completely different:
6f1d4bd63b31e53d3bb99bada9ac2f7dbf51e3b2d1d0d1a755a44050be9a946b
The art of cryptography
And this is precisely when we arrive at the most important use case of photography for us: blockchain. Blockchain is a digital open ledger, which every cryptocurrency is based on, and this is why everything can run smoothly with no central authority. Let’s see how the concept of cryptography first entered the world of blockchain.
Digital signatures
You probably don’t know it, but every time you send a transaction on a blockchain, it’s more like signing a contract. Why? Instead of using pen and paper, you create a digital signature with a private key. The produced signature is proof that you’re the owner of this wallet and would like to initiate a transaction. This way no one else can forge it and steal your funds.
Adresses
Cryptocurrency addresses are derived from public keys. They are like bank account numbers, but for crypto. Creating an address is a straightforward process for the user. Under the hood, many things are going on. In short, a public key is fed through a hashing algorithm. The result is a much shorter and more user-friendly identifier. This is “where” your funds go. The best thing? It’s impossible to reverse-engineer and reveal your private key.
The chain reaction
For every block in a blockchain, there’s a unique hash and a hash of the previous block. This is what connects the blocks and creates a chain, hence the name blockchain. If you were to change one data in a block, you don’t have to change just the block but the entire sequence of blocks that come after it, which is impossible unless you control the majority of mining power of a network.
A word on security
Security is a topic you should never skip. What’s the use of your knowledge if you don’t have any funds to manage? It’s important to keep your private key safe in the form of a seed phrase or any other. Losing it means losing access to each and every dollar you hold on-chain. Here are a few tips to stay safe.
Use a hardware wallet, which stores your private key offline and offers far superior protection from hacks.
Backup your key by writing it down and keeping it in a secure place. Never screenshot it and store it online for better security.
Just don’t share your keys. So trivial, right? Yet many people make this mistake again, whether it’s on accident or because of lack of basic knowledge. Don’t give up your wealth due to a stupid mistake.

Security is crucial when it comes to protecting your digital assets.
Wrapping up
At first, cryptography may seem intimidating, but it is the foundation on which not only the blockchain technology but also many real-world apps are built. The more you get around, the easier it will be for you to grasp the topic. And remember—practice makes perfect, so send your first transaction, use a blockchain explorer to check when it’s confirmed, and learn.
Next time you hear about cryptography, you’ll know it’s more than just a fancy word but an entire system guarding the digital realm.
Table of contents