Oct 20, 2024
Blockchain is a secure, decentralized ledger technology that records transactions transparently without a central authority. Originally developed for cryptocurrencies, it’s now revolutionizing industries like healthcare, finance, and supply chain by enhancing trust and security.
Every innovation begins with a simple problem. For centuries, humans relied on handshakes, signatures, and third parties to validate transactions. We trusted banks to guard our money, governments to maintain records, and notaries to certify documents. But what if there was a way to eliminate the middleman entirely and still maintain trust?
That's exactly what blockchain does. It's a technology that allows people to share and verify information without needing a central authority. And while it might sound complex, the core idea is surprisingly simple once you break it down.
Let's explore what blockchain really is, how it works, and why it's quickly becoming one of the most talked-about technologies in the world.
The Trust Problem Blockchain Solves
Think about the last time you sent money to someone. Maybe you used your bank's app or a service like PayPal. Behind the scenes, these companies verified your identity, checked your balance, and recorded the transaction. They acted as the middleman, and you paid fees for that service.
Now imagine a world where you could send money directly to someone else without any bank involved. The transaction would still be secure, transparent, and permanent. That's the promise of blockchain.
Blockchain removes the need for intermediaries by creating a shared, public record that everyone can see and verify. Instead of trusting one company or institution, you trust the system itself.

A blockchain is a ledger composed of blocks (like pages in a book), where each block is written once by a selected participant.
Breaking Down the Basics
At its core, blockchain is exactly what it sounds like—a chain made up of blocks. But what does that actually mean?
Blocks Are Like Digital Containers
Each block holds a collection of information. In the case of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, that information includes transaction details: who sent money, who received it, and how much was transferred.
But blocks aren't limited to financial data. They can store anything from medical records to supply chain information. Once a block is filled with data, it gets sealed and added to the chain.
The Chain Keeps Everything Connected
Here's where it gets interesting. Each new block contains a reference to the block before it. This creates a permanent, unbreakable link. If someone tries to alter information in an old block, the entire chain breaks, and the fraud becomes obvious.
It's like writing in permanent ink. Once something is recorded, it stays there forever.
Decentralization Changes Everything
Traditional systems store data in one place—a bank's server, a government database, or a company's cloud. If that system gets hacked or fails, the data can be lost or manipulated.
Blockchain works differently. Instead of one central database, thousands of computers around the world each hold a complete copy of the blockchain. These computers, called nodes, work together to verify and record new transactions.
If one computer gets compromised, the others catch the error. The system polices itself.
How a Blockchain Transaction Actually Happens
Let's walk through a real example. Suppose you want to send cryptocurrency to a friend using a platform like Swapped.com.
You Initiate the Transaction
You open your digital wallet and enter your friend's wallet address along with the amount you want to send. This creates a transaction request that gets broadcast to the blockchain network.
The Network Verifies Everything
Once your transaction is announced, nodes across the network start checking it. They confirm you have enough funds, verify the wallet addresses are valid, and ensure you're not trying to spend the same money twice.
This verification process is called consensus. The majority of nodes need to agree that your transaction is legitimate before it moves forward.
The Transaction Gets Locked Into a Block
After verification, your transaction gets bundled with others into a new block. Miners or validators—depending on the blockchain—compete to add this block to the chain by solving complex mathematical problems.
Once the block is added, your transaction is complete. The record is permanent and visible to anyone who wants to check the blockchain.
Your Friend Receives the Funds
The entire process might take a few seconds or a few minutes, depending on the blockchain. But once it's done, your friend has the money, and the transaction is locked into the public ledger forever.
Platforms like Swapped.com make this process simple and secure, with transparent fees and fast processing times. We handle the technical details so you can focus on what matters—sending and receiving crypto quickly and easily.
Why Blockchain Stands Out
Blockchain isn't perfect, but it offers some powerful advantages over traditional systems.
Security That's Hard to Beat
Every block is encrypted and linked to the one before it. Changing even one tiny detail would require altering every block that came after it—across thousands of computers simultaneously. That's virtually impossible.
Transparency Without Sacrificing Privacy
Anyone can view transactions on a public blockchain, but personal details remain hidden. Instead of names, the system uses wallet addresses—long strings of numbers and letters. You get accountability without exposing your identity.
Speed and Cost Savings
Traditional bank transfers, especially international ones, can take days and come with hefty fees. Blockchain transactions happen much faster and often cost far less because there's no middleman taking a cut.
With Swapped.com, we've minimized transaction fees even further, making it one of the most affordable ways to buy and sell crypto. Network fees still apply, but those go to validators who maintain the blockchain—not to us.
You Stay in Control
When you use blockchain, you control your assets directly. There's no bank that can freeze your account or government that can seize your funds without due process. You hold the keys, literally.
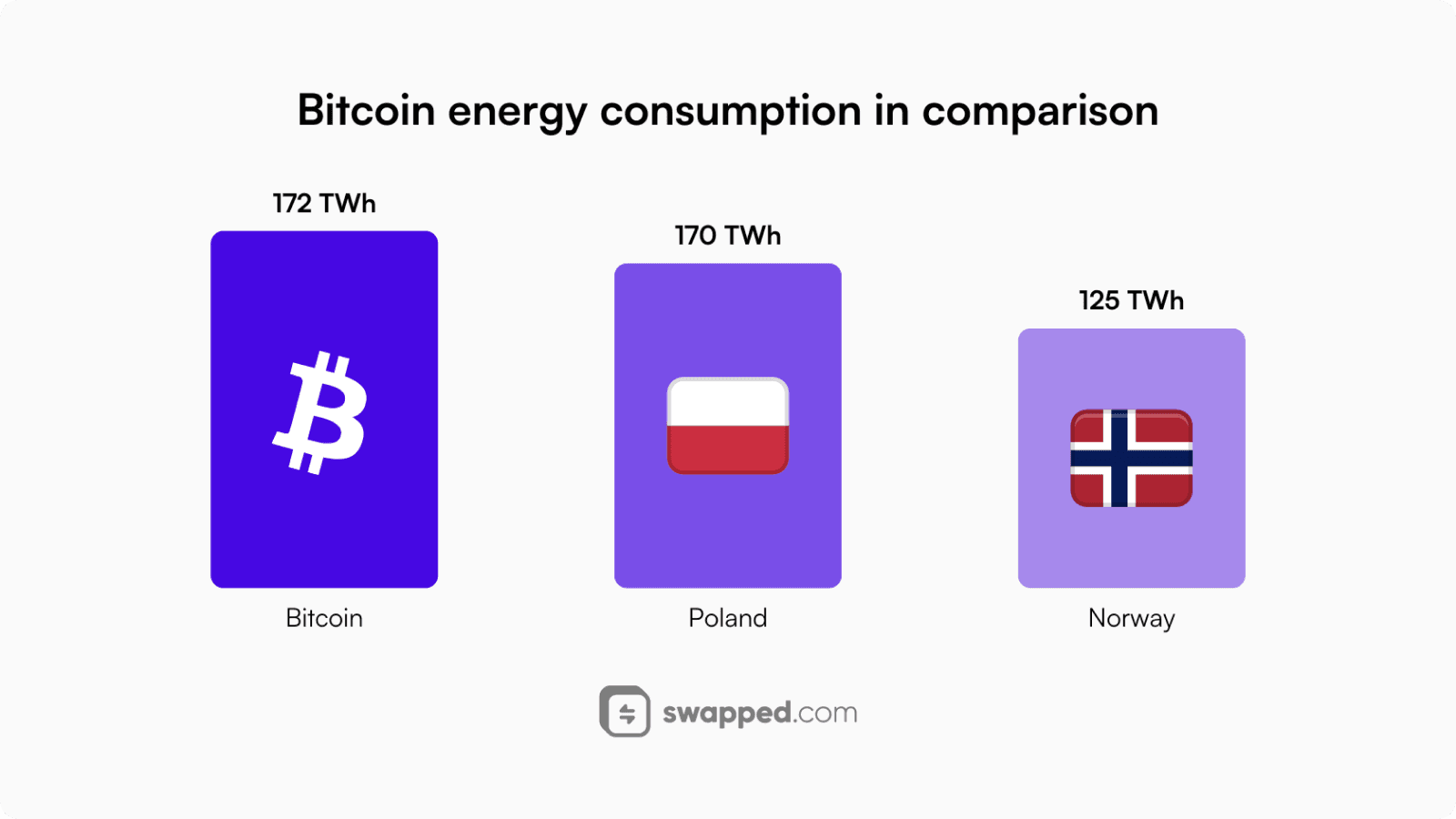
Bitcoin’s yearly energy consumption in comparison to other countries based on this study from December 5, 2023.
The Challenges Blockchain Still Faces
No technology is without its drawbacks, and blockchain is no exception.
Energy Use Can Be High
Some blockchains, like Bitcoin, require enormous amounts of energy to operate. Miners use powerful computers to solve puzzles and validate transactions, which consumes electricity. However, newer blockchains are adopting more energy-efficient methods.
Scaling Remains a Concern
As more people use a blockchain, the network can slow down. Bitcoin, for example, processes only a handful of transactions per second compared to thousands handled by traditional payment networks. Developers are working on solutions, but it's still a work in progress.
The Learning Curve Is Real
Blockchain involves unfamiliar terms like wallets, private keys, and hashes. For beginners, it can feel overwhelming. That's why platforms like Swapped.com exist—to simplify the experience and guide you through every step.
Regulations Are Still Evolving
Governments around the world are still figuring out how to regulate blockchain and cryptocurrencies. This uncertainty can make people hesitant to adopt the technology fully.
Simply put, blockchain is a chain of blocks, each containing data.
Is Blockchain the Same as Bitcoin?
Not quite. Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency that runs on blockchain technology. But blockchain itself is the underlying system—the foundation.
Think of it this way: blockchain is like the internet, and Bitcoin is like email. Email is just one application of the internet, just as Bitcoin is one application of blockchain. Other cryptocurrencies like Ethereum also use blockchain, and the technology has countless uses beyond digital money.
Why Blockchain Matters to You
You might be wondering, "Why should I care about blockchain?" Here's the truth: blockchain is quietly reshaping the world around you.
Financial systems are becoming faster and cheaper. Supply chains are becoming more transparent. Artists are gaining more control over their work. And individuals are reclaiming ownership of their data.
Whether you're looking to buy your first cryptocurrency, explore new investment opportunities, or simply understand the technology shaping the future, blockchain is worth your attention.
And if you're ready to take your first step, Swapped.com makes it easy. We offer a simple, secure, and affordable way to buy and sell crypto without the hassle. You stay in control of your assets, and we provide the tools and support you need to navigate the world of blockchain with confidence.
Resources
If you're interested in diving deeper and expanding your knowledge of blockchain, here are some suggestions:
Table of contents