What is a fork in crypto?
Cryptocurrency forks are major decisions and the result of a disagreement between community members. It's an event of great significance that you can either profit or lose money from.
Written by Kacper Tomasiak
Feb 20, 2025
Cryptocurrencies aren’t created perfect, and they require constant upgrades. Community and founders sporadically see things differently, which may also be a reason for a crypto fork to happen. There were many forks in crypto history, and cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin Cash or Ethereum Classic were the result of such an event.
What exactly is a fork, and why does it hold such significance in a cryptocurrency’s history? Let’s break down what a fork is, why it happens, and how it impacts crypto investors.
What is actually a fork?
A fork refers to a difference in a blockchain’s history. This is what happens when there is a disagreement about network rules or when an upgrade occurs.
Blockchains are decentralized; therefore, thousands of nodes must agree on the network’s rules. Before new rules take effect, some participants choose to follow the new ones, whereas others decide to stick to the original rules, leading to a split or, in this case, a fork.
Types of forks
Crypto forks may also be an effect of software updates, with some being minor (soft forks) and others introducing large changes, making the previous version obsolete.
Soft forks
A soft fork is a blockchain update that is compatible with previous versions. In this example, nodes that aren’t updated to the latest versions can still interact with the new upgraded chain.
In essence, soft forks present new rules that do not violate the old ones. Let’s say that the maximum block size of a chain was 1MB, and a soft fork introduces an upgrade decreasing the size. Older nodes will still accept these smaller blocks.
Soft forks allow the network to be united so there is not a split into multiple chains. Basically, they encourage upgrades but do not enforce them on node operators.
Hard forks
A hard fork is an instantaneous and absolute change that doesn’t make the new blockchain compatible with previous versions. It causes a permanent split of the chain and creates two separate networks operating independently on their own.
When a hard fork takes place, some network participants adjust to the new rules while others favor the old ones. This disagreement creates two separate cryptocurrencies with distinct transaction histories starting from the fork date.
Hard forks can help with significant improvements and give users a choice of using the network before or after the changes. On the other hand, rigid forks cause a division between communities and confusion among users not familiar with the project.

Soft and hard forks fundamentally differ.
Why do forks happen?
When it comes to forks, there isn’t just one answer. There are plenty of reasons why they happen and that you should be aware of.
Security and performance upgrades
Some forks are required to fix bugs, improve security, or enhance network performance. A wonderful example is Ethereum’s London Hard Fork, which changed transaction fees to reduce congestion.
Scaling improvements
When changes like block size or block time are made, this leads to a fork. A notable fork is Bitcoin Cash, which increased the block size in contrast to the original network—Bitcoin.
Divergent visions
Members of crypto communities often have divergent visions in mind. For instance, Ethereum Classic was created because some community members were advocates for blockchain immutability, refusing to reverse transactions because of a hack.
Impact of forks on investors
A fork isn’t a reckless decision and involves consequences that the community and developers have to deal with. These can become challenging and may contribute to the project’s downfall.
New coins
A hard fork results in free coins for existing holders. As a holder, you get an equal amount of coins on the new chain, as was the case with BTC and BCH.
Market volatility
Forks in most cases cause uncertainty, and this emotion leads to price fluctuation and increased volatility. This may be a combination of confusion among potential investors, outflow of capital from the old chain and fear about the project's future. Just after Bitcoin Cash forked, Bitcoin initially dropped before recovering.
Chain support
Not all exchanges and wallets will support the newly forked coins immediately. Investors should watch for new announcements and refrain from making decisions that could cause regret at a later date.
Concerns
Instead of fixing issues, forks can create vulnerabilities that not only affect the new chain but also the old one. It’s always best to understand what you’re investing in and the risk you’re taking. Sometimes it’s better to sell coins, wait out the uncertain period, and buy again later.
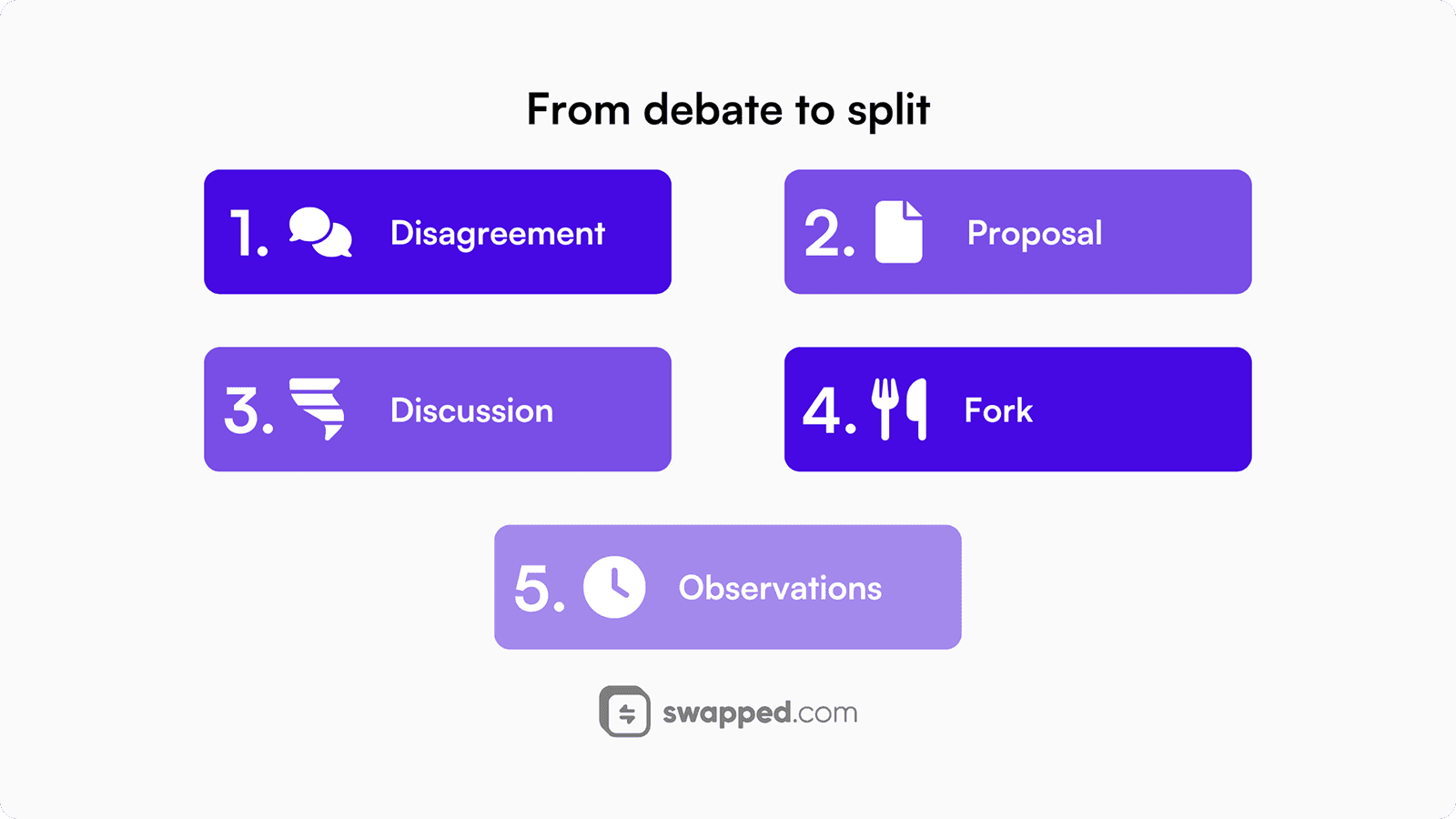
A crypto fork is a time-intensive decision and could take weeks or months to play out.
Notable forks in crypto
In the entire history of cryptocurrencies, there were two particularly important forks. Let’s take a closer look.
Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash
Not a long time after Satoshi created Bitcoin, a problem of scalability was brought up. Some community members felt like in order to progress and gain mass adoption, Bitcoin needs to be faster and cheaper. Bitcoin Cash, a Bitcoin fork, was the solution to this dilemma with an increased block size of up to 8MB. As of then, it was a major breakthrough, but right now Bitcoin still remains the king, and there are much better solutions to scalability problems.
Ethereum and Ethereum Classic
In 2016, Ethereum enthusiasts faced a major challenge. Funds were drained from a DAO, and the community was split over whether to reverse the theft by implementing the hard fork. Some argued that code is law and the network should just move on. The majority, however, was in favor of reversing the hack; thus, what is known now as Ethereum was created, and the unaltered old chain was renamed to Ethereum Classic.
Are forks good or bad?
So what is the final verdict then—are forks good or bad for the crypto space?
Benefits
There are real benefits to implementing forks, like improving the network and driving innovation. They also enhance security and performance as well as allow different versions to coexist, rendering a choice for users.
Challenges
Crypto forks also have a darker side. Unfortunately, they cause divisions among the community and confuse investors that were once willing to put money in the coin. The time period around the fork event is usually volatile, and price action may shake out even the greatest supporters.
Summary
Forks are an essential part of blockchain evolution. They allow for new upgrades and the community voices to be heard. As a crypto user and an investor, understanding what forks are, why they happen, and how they work is key to making well-researched decisions and securing your assets during uncertain times. Which cryptocurrency do you think will be the next to fork?
Resources
If you're interested in diving deeper and expanding your knowledge of crypto forks, here are some suggestions: