What is Ethereum (ETH)?
Ethereum, launched in 2015, changed blockchain forever by enabling smart contracts and decentralized apps. Its currency, Ether, is what keeps the ecosystem alive and secures the network.
Written by Kacper Tomasiak
Nov 17, 2024
When Bitcoin was introduced in 2009, it was a revolution prepared to overtake the traditional financial system. While Bitcoin helped create the blockchain technology, it was Ethereum that expanded the horizons far beyond just the vision of digital gold. Ethereum enabled a world with decentralized applications and smart contracts—Ether was ready to reshape industries.
Introduction to blockchain
Blockchain technology really changed the game by introducing a way to record transparent, secure, and decentralized transactions. Blockchains are not reliant on banks or intermediaries. Instead, they use a network of computers to verify each transaction and store it in blocks, hence the name. These blocks are linked together, forming a chain nearly impossible to alter. The technology was first used in Bitcoin and is the foundation of a new era where trust is built right into the code.
The founder of Ethereum
Vitalik Buterin is a programmer and the face behind Ethereum, although he is just a co-founder and many more were involved. He was born in 1994, and in his early years, he discovered blockchain technology. He immediately saw the immense potential of Bitcoin and what it will become in the future. With the creation of Ethereum, Buterin showed the world the concept of smart contracts—self-executing agreements that run without anyone involved. It was this idea that eventually led to unlocking the possibilities of programmable applications on blockchain.
A new kind of Internet
To understand why Ethereum gained popularity as quickly as it did, you need to imagine a world where code is law. Need to rent an apartment? A smart contract could ensure you get the keys once a payment is made. No unnecessary things need to be done.
The idea spread like wildfire. Ethereum was kind of like the American dream. Developers were flooding the ecosystem with new dApps that could do everything from lending money to running online marketplaces. Ethereum was a small project no more; it was a blue chip aiming for the Bitcoin spot.
More than just digital gold
Ethereum (ETH) wasn’t just another cryptocurrency but an essential component for the Ethereum network to function. Want to execute a smart contract? You’ll need ETH to cover the gas fees. Every interaction, whether it was launching a new dApp or minting an NFT, needed this digital fuel. Paying these costs in exchange for a secure network suited for your needs is worth it. ETH ensures that the network continues to work for the years to come.
Ethereum is different for everyone. For developers and tech enthusiasts, it’s a tool. For artists, it’s where they can sell their artwork and connect with a global audience. In other ways, the ETH token is a bet on the future of the internet for investors, while it’s a platform free of third parties for businesses.
How Ethereum works
Ethereum, while being a very complex network, manages to be easy to use for the end user. Here’s a breakdown of the essential features that make Ethereum a go-to platform for DeFi and NFTs.
Understanding gas fees
No matter what, every transaction on the Ethereum blockchain requires a gas fee, paid in ETH. Gas fees are what keep the network running. How are gas fees calculated? The more complex the interaction is, the higher the gas fee. While sudden spikes in traffic have been a problem for smaller wallets, Ethereum’s developers are working on a solution to make transactions more affordable.

Usage fees for the most popular networks compared to ETH. Average fees as of Nov 12, 2024.
What are smart contracts?
Smart contracts are the innovation Ethereum introduced. Simply put, they are like contracts in the real world, but written in code and self-executed. Think of them like “if-then” statements. These contracts remove the need for any third parties to be involved.
What are decentralized applications?
The idea behind dApps is as simple as it gets. These decentralized applications are all about providing mainly financial services to network users while maintaining absolute transparency and enabling transactions without a middleman. Every action and all the rules are immutable and saved on the blockchain for everyone to see.
How dApps work
Decentralized applications usually run on blockchain platforms that possess smart contract capabilities like Ethereum. To better understand how they work, picture a vending machine selling drinks. Once you put in the correct amount of money, the machine automatically gives you a drink—no need for a cashier. This is exactly how dApps work—you can always expect a predictable predetermined outcome, whether it’s swapping tokens or buying an NFT, based on your actions without the need for human intervention.
A step into the future
Fast forward to 2022, Ethereum had evolved but still lacked the modern technology. Transactions were faster, yes, but the network wasn’t energy-efficient at all. The old consensus mechanism was in place, just like in Bitcoin, where miners solved puzzles to validate transactions, and they were rewarded with coins.
That’s the year when the Ethereum team pulled off “The Merge”, the most anticipated blockchain upgrade in history. The upgrade meant transitioning to Proof of Stake, a consensus mechanism that was much more energy-efficient. As a result, Ethereum’s energy consumption dropped by 99%, and the issuance of new tokens fell off a cliff. The Merge initiated a sequence of upgrades that would change Ethereum for the better forever.
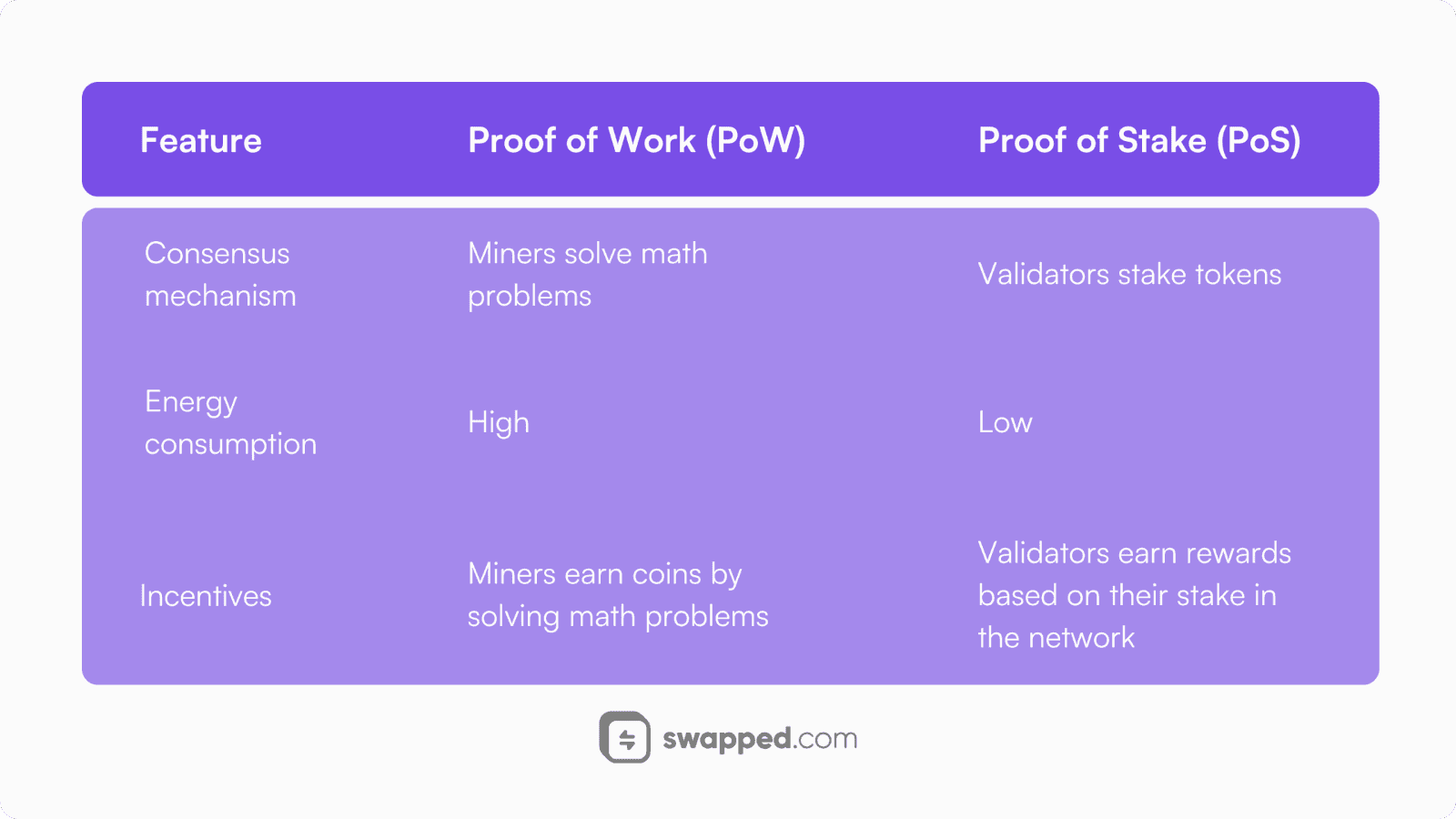
A comparison between Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
Challenges and competitors
Ethereum isn’t the only tool available. Blockchains like Solana with even cheaper and faster transactions are in the race. Ethereum has rightly faced criticism for enormously high gas fees during peak traffic—a deal-breaker for newcomers wanting to try out the network. However, Ethereum is still evolving, and there are numerous Layer 2 solutions available on the market. These solutions, like Zero Knowledge rollups, mean lower fees and faster transactions.
How to buy and store ETH
To buy Ethereum, you’ll need a platform that lets you buy cryptocurrencies. For instance, you can use a crypto on-ramp like Swapped.com, which supports several payment methods such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, credit cards, PayPal or bank transfer. Just choose the amount, the payment method, and your ETH will be delivered in minutes.
As for storing ETH, it’s best to set up a digital wallet. You can either download an app or purchase a physical divide known as a hardware wallet. Hardware wallets such as a Ledger or a Trezor add an extra layer of security by keeping your coins offline.
What's next?
Inside the Ethereum community, there’s talk of sharding—a solution to Ethereum’s high fees and slow transactions. The roadmap is vast for the years to come, and while some ideas aren’t set in stone yet, one thing is sure: Ethereum will remain number two in the foreseeable future.
Ethereum was built from nothing and achieved the unthinkable. Every transaction, every contract adds another chapter to this great story about innovation as the network continues to evolve. It’s not just a blockchain but a movement for a decentralized, democratized, and accessible future.
Resources
If you're interested in diving deeper and expanding your knowledge of Ethereum, here are some suggestions: